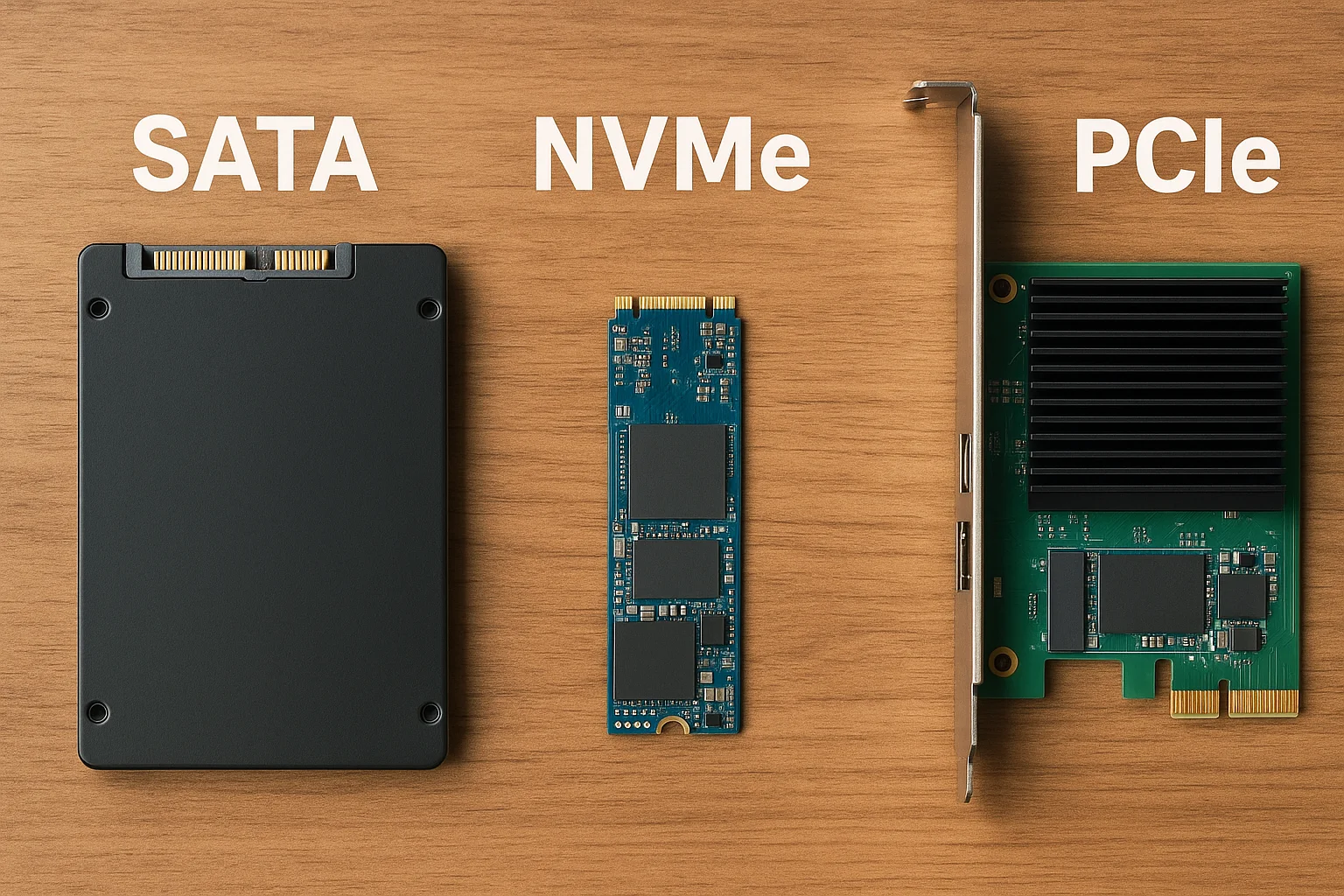
Differences Between SATA, NVMe, and PCIe Storage Technologies
SATA, NVMe, and PCIe are terms often mentioned in the world of storage—but what do they really mean, and how do they differ? In this post, we break down each technology, explain how they work, compare their performance, and help you decide which one suits your needs best, whether you're building a PC, gaming, editing videos, or upgrading your laptop.